FREE BPI PRACTICE EXAMPUT YOUR HOME PERFORMANCE BUSINESS ON ROCKET FUELENERGY AUDITOR NEWSLETTERGet the only Energy Auditor Marketing Newsletter with monthly strategies and tactics to grow your home performance business.
The main topics of the BPI BA exam are listed out below. Click on a link that interests you, or you need some brushing up on to learn more on each subject.
1. Building Science Fundamentals 1a. Basic terms and definitions 1b. Principals of energy, air & moisture 1c. Combustion science 2. Buildings and Their Systems 2a. Building components 2b. Conservation strategies 2c. Comprehensive building assessment process 2d. Design considerations 3. Measurement and Verification of Building Performance 3a. Applied diagnostics and troubleshooting 4. BPI National Standards and Project Specifications 4a. Comprehensive building assessment 5. Analyzing Buildings Systems 5a. Comprehensive building assessment 5b. Appliances and lighting 6. Conduct and communications 6a. Conservation strategies |
Passing the BPI Exam With Energy Auditor TrainingBPI Written Exam - Section 2 Buildings and Their Systems3. Identify Basic Structural Components of Residential Construction
There are 4 main structural components of a home, together they are known as the building shell.
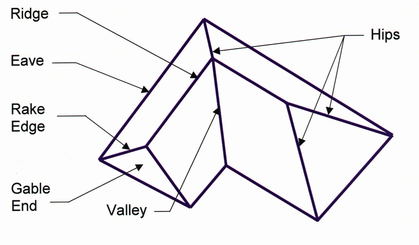
1. Roof - truss designs are scissor truss, hip and vault.
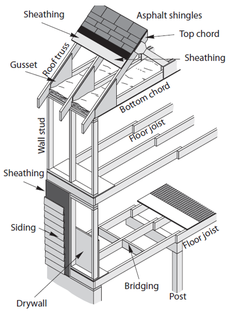
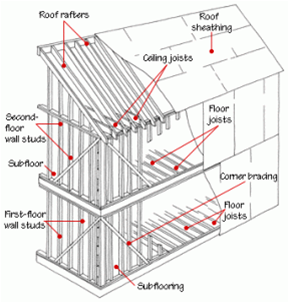
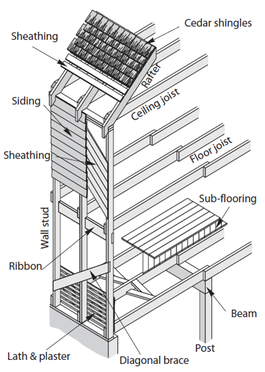
2. Vertical supports - for walls use either 2x4 or 2x6 wood studs. For energy efficiency, more insulation can fit in between a 2x6 stud and reduces the thermal bridging that occurs more often in a 2x4 stud. Other components of a vertical support include: headers, jams, kind studs and threshold. Rim joist support the main level floor between the foundation and the vertical supports. Band joists support the upper level floor. Balloon framing is a common type of construction pre-1960s, where the walls are open from the basement to the attic.
Platform framing
Balloon framing
3. Floors - include the floor joist, subfloor, carpet, laminate, tile or wood.
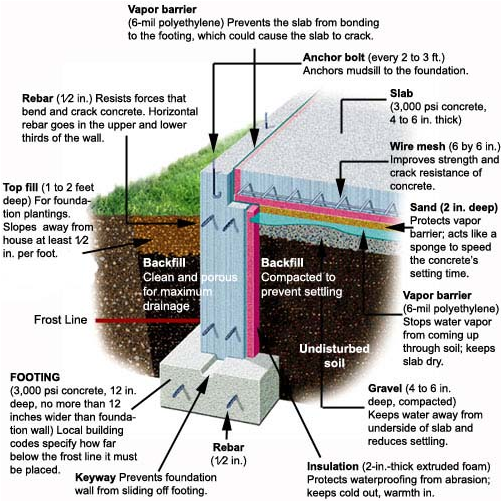
4. Foundation - is the concrete slab, footing, gravel, keyway, rebar, anchor bolts, wire mesh, sand and vapor barrier. It can also include the crawlspace if there is one present with piers and beams under the floor or stem wall.
Next Section2a. Building Components
2b. Conservation Strategies
2c. Comprehensive Building Assessment Process
2d. Design considerations
|
- HOME
- PRACTICE EXAMS
- NEWBIES
-
STUDY GUIDES
-
BPI WRITTEN EXAM
>
-
Section 1 Building Science Fundamentals
>
-
1a. Basic Terms & Definitions
>
- 1. Airflow in Buildings
- 2. Equipment Efficiencies
- 3. Power and Energy
- 4. Effective Leakage Area
- 5. Area Weighted R-Value
- 6. Baseload / Seasonal Energy Use
- 7. Driving Forces (Including Natural and Mechanical)
- 8. Behavior of Radiation
- 9. Thermal Resistance / Transmittance: R and U Values
- 10. Latent / Sensible Heat
- 11. Total Equivalent Length
- 12. Dehumidification / Humidification
- 13. Convert Pressure Units
- 14. Thermal Bridges
- 15. Pressure Boundary
- 16. Stack Effect
- 17. Exfiltration and Infiltration
- 18. Natural / Mechanical Ventilation
- 19. Net Free Area
- 20. Input & Output Capacity
- 21. Peak Electrical Demand
- 22. Permeability and Perm Rating
- 23. Standby Loss
- 24. IAQ (indoor air quality): Moisture, CO, Dust
-
1b. Principals of Energy, Air & Moisture Thermodynamics
>
- 1. Thermodynamics: Conduction, Convection, Radiation, ΔT
- 2. Factors That Affect Insulation Performance
- 3. BPI certification online with BPI practice exams and study guides.
- 4. Heat Gain / Loss
- 5. Power and Energy
- 6. Moisture Transport Mechanisms
- 7. Identify Areas of Highest Relative Humidity
- 8. Principles of Combustion
- 1c. Combustion Safety >
-
1a. Basic Terms & Definitions
>
-
Section 2 Buildings and Their Systems
>
-
2a. Building Components
>
- 1. Identify basic duct configurations and components
- 2. Identify Basic Hydronic Distribution Configurations and Components
- 3. Identify Basic Structural Components of Residential Construction
- 4. Thermal Boundaries and Insulation Applications
- 5. Basic Electrical Components and Safety Considerations
- 6. Basic Fuel Delivery Systems and Safety Considerations
- 7. Basic bulk water management components (drainage plumbing gutters sumps etc)
- 8. Vapor barriers/retarders
- 9. Radiant Barrier Principles and Installations
- 10. Understand Fenestration Types and Efficiencies
- 11. Understand Issues Involved With Basements, Crawlspaces, Slabs, Attics, Attached Garages, Interstitial Cavities, and Bypasses
- 12. Understand Issues Involved With Ventilation Equipment
- 13. Understand Basic Heating / Cooling Equipment Components Controls and Operation
- 14. Understand Basic DHW Equipment Components Controls and Operation
- 15. Identify Common Mechanical Safety Controls
- 16. Identify Insulation Types and R-Values
- 17. Understand Various Mechanical Ventilation Equipment and Strategies: Spot, ERV, HRV
-
2b. Conservation Strategies
>
- 1. Appropriate Insulation Applications and Installation Based On Existing Conditions
- 2. Opportunity for ENERGY STAR Lighting and Appliances
- 3. Identify Duct Sealing Opportunities and Applications
- 4. Understand Importance of Air Leakage Control and Remediation Procedures
- 5. Blower Door-Guided Air Sealing Techniques
- 6. Water Conservation Devices and Strategies
- 7. Domestic Hot Water (DHW) Conservation Strategies
- 8. Heating & Cooling Efficiency Applications
- 9. Proper Use of Modeling to Determine Heating and Cooling Equipment Sizing and Appropriate Energy
- 10. Understand the Use of Utility History Analysis in Conservation Strategies
- 11. Appropriate Applications For Sealed Crawlspaces Basements and Attics
- 12. Identify / Understand High Density Cellulose
- 13. Appropriate Applications for Fenestration Upgrades Including Modification or Replacement
- 2c. Comprehensive Building Assessment Process >
-
2d. Design Considerations
>
- 1. Appropriate Insulation Applications Based On Existing Conditions
- 2. Understand Fire Codes as Necessary to Apply Home Performance in a Code-Approved Manner
- 3. Understand / Recognize Building Locations Where Opportunities for Retrofit Materials
- 4. Understand Climate Specific Concerns
- 5. Understand Indoor Environment Considerations for the Environmentally Sensitive
- 6. Understand Impact of Building Orientation, Landscape Drainage, and Grading
- 7. Opportunity Potential Renewable Energy Applications: Geothermal, Photovoltaic, Wind
- 8. Understand Impact of Shading on Heating / Cooling Loads
- 9. Awareness for Solar Gain Reduction / Solar Gain Opportunities
- 10. Understand Need for Modeling Various Options For Efficiency Upgrades
-
2a. Building Components
>
-
Section 3 Measurement & Verification of Building Performance
>
-
Section 3a Measurement & Verification of Building Performance
>
- 1. Air Leakage Test Results
- 2. Understand Building Shell / Envelope Leakage
- 3. Apply Fundamental Construction Mathematics and Unit Conversions
- 4. Calculate Building Tightness Levels (Minimum Ventilation Requirements)
- 5. Calculate Heating Degree Days and Cooling Degree Days
- 6. Identify Proper Appliance and Combustion Appliance Venting
- 7. Ventilation calculations and strategies
- 8. Proper methods for identifying / testing fuel leaks
- 9. Blower door setup, accurate measurement and interpretation of results
- 10. Combustion Appliance Zone (CAZ): depressurization, spillage, draft, Carbon Monoxide (ambient and flue)
- 11. Carbon Monoxide (CO) evaluation: ambient
- 12. Proper applications and use of temperature measuring devices
- 13. Pressure pan and room to room pressure diagnostics
- 14. Recognize contributing factors to comfort problems
- 15. Inspect for areas containing moisture or bulk water in undesirable locations
- 16. Understand and inspect for basic electric safety (e.g. frayed wires, open boxes, etc)
-
Section 3a Measurement & Verification of Building Performance
>
-
Section 4 BPI National Standards & Project Specifications
>
- 1. Understand applicability content and intent of BPI National Standards – Do no harm, make buildings more healthy, comfortable, durable and energy efficient
- 2. Recognize need for a professional local/state/national codes evaluation
- 3. Be able to specify appropriate materials and processes needed for building performance projects
-
Section 5 Analyzing Buildings Systems
>
- 1. Recognize need for air sealing measures and their impact on other building systems
- 2. Recognize need for mechanical equipment improvements
- 3. Understand blower door use for identifying critical air sealing areas
- 4. Apply blower door test results and Building Tightness Limit (minimum ventilation requirements) in development of improvement strategies
- 5. Using combustion analysis and safety testing results to develop appropriate recommendations
- 6. Determine appropriate method for assessing wall insulation levels
- 7. Equipment control strategies for maximizing occupant comfort and minimizing energy consumption
-
Section 6 Conduct and Communications
>
- 6a. Conservation strategies
-
6b. Personal Safety & Work Practices
>
- 1. Locations in which to identify indoor air quality issues
- 2. Material Safety Data Sheets
- 3. Isolation procedures for household pollutants
- 4. Practice building science within your limits of professional competency
- 5. Precautions when working around chemical biological and other potential hazards
- 6. Understand role and responsibilities of the building analyst professional
-
Section 1 Building Science Fundamentals
>
- BPI FIELD EXAM >
- BLOWER DOOR TEST >
- BPI BUILDING ANALYST STANDARDS >
-
BPI WRITTEN EXAM
>
- ESSENTIALS
- AFTER THE EXAM
- NEWSLETTER
- BLOG
|
Copyright 2023 Building Science Training Center LLC
|