FREE BPI PRACTICE EXAMGET THE NEWSLETTERTo get FREE updates and information about all the BPI Exams, please enter your name and email below.
BPI STUDY GUIDES |
Passing the BPI Exam With Energy Auditor TrainingBPI Written Exam - Section 5 Analyzing Buildings' Systems5. Using combustion analysis and safety testing results to develop appropriate recommendationsEnergy auditors will measure the room size for combustion equipment, venting, test gas leaks, draft, spillage and undiluted CO for combustion safety tests. All these tests have standards and thresholds that need to be met to meet safety requirements. Here's what to recommend if any of the combustion tests fail.
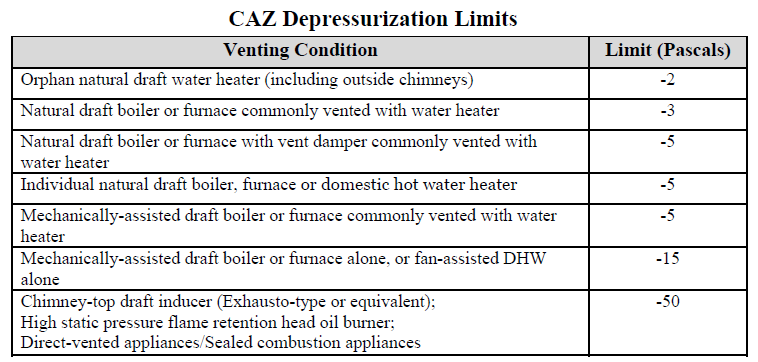
A preliminary and post-installation safety inspection of all combustion appliances must Minimum room size for combustion equipmentSee Failed CAZ below.
Gas leaksThe entire gas/propane line must be examined and all leaks repaired. Particular care The BPI Standards above say that all gas leaks should be repaired if a leak is found. As energy auditors if you are not qualified to do this, you need to inform the homeowner and strongly encourage them to call a plumber, HVAC contractor or handyman to repair the leak rather than yourself. You could also encourage the homeowner to stop using the appliance or shut the gas valve off upstream of the leak. Also make sure CO detectors are installed and working.
Failed CAZFailed CAZ could be the result of not enough room venting. A room size calculation should be done to determine if the existing vents are large enough for the combustion appliances in the room. Sometimes replacing the furnace or water heater closet door with a slotted door will fix a failed CAZ. Sometimes you will need to recommend cutting a new vent in the wall to the outside. Sometimes you will need to recommend relocating the dryer if that's what is causing the strong pull of combustion gases back into the home.
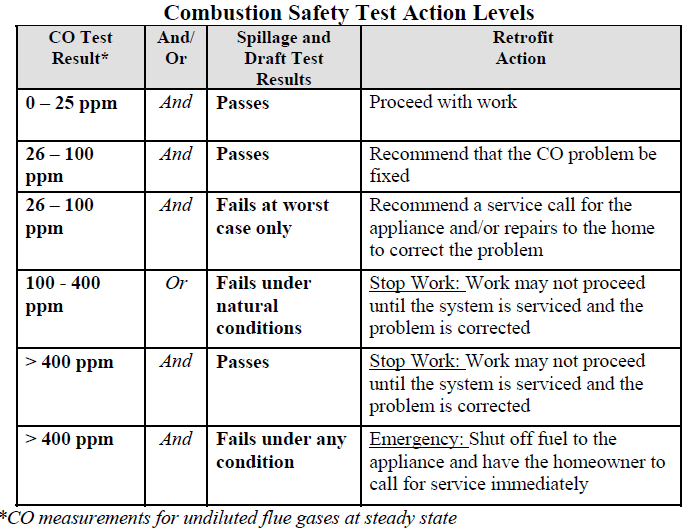
Ambient COAmbient CO. Monitor the ambient CO in the breathing zone during the test procedure and abort the Sometimes a handyman is the best contractor to call, sometimes it's a HVAC contractor or plumber, but as energy auditors we need to recommend the appropriate trade get called to fix the problem and strongly encourage the homeowner to ventilate the space with open windows and check that CO detectors are installed and working before you leave the house.
High undiluted COAt least one CO detector meeting UL-2034 requirements shall be installed according to If the CO in any appliance is measured greater than 100 ppm during diagnostic testing, or Level I Action - 100 ppm to 300 ppm as measured you must install a carbon Failed draft testMeasure Worst Case Spillage, Draft, CO. Fire the appliance with the smallest Btu capacity first, 5a. Comprehensive building assessment
5b. Appliances and lighting
|
- HOME
- PRACTICE EXAMS
- NEWBIES
-
STUDY GUIDES
-
BPI WRITTEN EXAM
>
-
Section 1 Building Science Fundamentals
>
-
1a. Basic Terms & Definitions
>
- 1. Airflow in Buildings
- 2. Equipment Efficiencies
- 3. Power and Energy
- 4. Effective Leakage Area
- 5. Area Weighted R-Value
- 6. Baseload / Seasonal Energy Use
- 7. Driving Forces (Including Natural and Mechanical)
- 8. Behavior of Radiation
- 9. Thermal Resistance / Transmittance: R and U Values
- 10. Latent / Sensible Heat
- 11. Total Equivalent Length
- 12. Dehumidification / Humidification
- 13. Convert Pressure Units
- 14. Thermal Bridges
- 15. Pressure Boundary
- 16. Stack Effect
- 17. Exfiltration and Infiltration
- 18. Natural / Mechanical Ventilation
- 19. Net Free Area
- 20. Input & Output Capacity
- 21. Peak Electrical Demand
- 22. Permeability and Perm Rating
- 23. Standby Loss
- 24. IAQ (indoor air quality): Moisture, CO, Dust
-
1b. Principals of Energy, Air & Moisture Thermodynamics
>
- 1. Thermodynamics: Conduction, Convection, Radiation, ΔT
- 2. Factors That Affect Insulation Performance
- 3. BPI certification online with BPI practice exams and study guides.
- 4. Heat Gain / Loss
- 5. Power and Energy
- 6. Moisture Transport Mechanisms
- 7. Identify Areas of Highest Relative Humidity
- 8. Principles of Combustion
- 1c. Combustion Safety >
-
1a. Basic Terms & Definitions
>
-
Section 2 Buildings and Their Systems
>
-
2a. Building Components
>
- 1. Identify basic duct configurations and components
- 2. Identify Basic Hydronic Distribution Configurations and Components
- 3. Identify Basic Structural Components of Residential Construction
- 4. Thermal Boundaries and Insulation Applications
- 5. Basic Electrical Components and Safety Considerations
- 6. Basic Fuel Delivery Systems and Safety Considerations
- 7. Basic bulk water management components (drainage plumbing gutters sumps etc)
- 8. Vapor barriers/retarders
- 9. Radiant Barrier Principles and Installations
- 10. Understand Fenestration Types and Efficiencies
- 11. Understand Issues Involved With Basements, Crawlspaces, Slabs, Attics, Attached Garages, Interstitial Cavities, and Bypasses
- 12. Understand Issues Involved With Ventilation Equipment
- 13. Understand Basic Heating / Cooling Equipment Components Controls and Operation
- 14. Understand Basic DHW Equipment Components Controls and Operation
- 15. Identify Common Mechanical Safety Controls
- 16. Identify Insulation Types and R-Values
- 17. Understand Various Mechanical Ventilation Equipment and Strategies: Spot, ERV, HRV
-
2b. Conservation Strategies
>
- 1. Appropriate Insulation Applications and Installation Based On Existing Conditions
- 2. Opportunity for ENERGY STAR Lighting and Appliances
- 3. Identify Duct Sealing Opportunities and Applications
- 4. Understand Importance of Air Leakage Control and Remediation Procedures
- 5. Blower Door-Guided Air Sealing Techniques
- 6. Water Conservation Devices and Strategies
- 7. Domestic Hot Water (DHW) Conservation Strategies
- 8. Heating & Cooling Efficiency Applications
- 9. Proper Use of Modeling to Determine Heating and Cooling Equipment Sizing and Appropriate Energy
- 10. Understand the Use of Utility History Analysis in Conservation Strategies
- 11. Appropriate Applications For Sealed Crawlspaces Basements and Attics
- 12. Identify / Understand High Density Cellulose
- 13. Appropriate Applications for Fenestration Upgrades Including Modification or Replacement
- 2c. Comprehensive Building Assessment Process >
-
2d. Design Considerations
>
- 1. Appropriate Insulation Applications Based On Existing Conditions
- 2. Understand Fire Codes as Necessary to Apply Home Performance in a Code-Approved Manner
- 3. Understand / Recognize Building Locations Where Opportunities for Retrofit Materials
- 4. Understand Climate Specific Concerns
- 5. Understand Indoor Environment Considerations for the Environmentally Sensitive
- 6. Understand Impact of Building Orientation, Landscape Drainage, and Grading
- 7. Opportunity Potential Renewable Energy Applications: Geothermal, Photovoltaic, Wind
- 8. Understand Impact of Shading on Heating / Cooling Loads
- 9. Awareness for Solar Gain Reduction / Solar Gain Opportunities
- 10. Understand Need for Modeling Various Options For Efficiency Upgrades
-
2a. Building Components
>
-
Section 3 Measurement & Verification of Building Performance
>
-
Section 3a Measurement & Verification of Building Performance
>
- 1. Air Leakage Test Results
- 2. Understand Building Shell / Envelope Leakage
- 3. Apply Fundamental Construction Mathematics and Unit Conversions
- 4. Calculate Building Tightness Levels (Minimum Ventilation Requirements)
- 5. Calculate Heating Degree Days and Cooling Degree Days
- 6. Identify Proper Appliance and Combustion Appliance Venting
- 7. Ventilation calculations and strategies
- 8. Proper methods for identifying / testing fuel leaks
- 9. Blower door setup, accurate measurement and interpretation of results
- 10. Combustion Appliance Zone (CAZ): depressurization, spillage, draft, Carbon Monoxide (ambient and flue)
- 11. Carbon Monoxide (CO) evaluation: ambient
- 12. Proper applications and use of temperature measuring devices
- 13. Pressure pan and room to room pressure diagnostics
- 14. Recognize contributing factors to comfort problems
- 15. Inspect for areas containing moisture or bulk water in undesirable locations
- 16. Understand and inspect for basic electric safety (e.g. frayed wires, open boxes, etc)
-
Section 3a Measurement & Verification of Building Performance
>
-
Section 4 BPI National Standards & Project Specifications
>
- 1. Understand applicability content and intent of BPI National Standards – Do no harm, make buildings more healthy, comfortable, durable and energy efficient
- 2. Recognize need for a professional local/state/national codes evaluation
- 3. Be able to specify appropriate materials and processes needed for building performance projects
-
Section 5 Analyzing Buildings Systems
>
- 1. Recognize need for air sealing measures and their impact on other building systems
- 2. Recognize need for mechanical equipment improvements
- 3. Understand blower door use for identifying critical air sealing areas
- 4. Apply blower door test results and Building Tightness Limit (minimum ventilation requirements) in development of improvement strategies
- 5. Using combustion analysis and safety testing results to develop appropriate recommendations
- 6. Determine appropriate method for assessing wall insulation levels
- 7. Equipment control strategies for maximizing occupant comfort and minimizing energy consumption
-
Section 6 Conduct and Communications
>
- 6a. Conservation strategies
-
6b. Personal Safety & Work Practices
>
- 1. Locations in which to identify indoor air quality issues
- 2. Material Safety Data Sheets
- 3. Isolation procedures for household pollutants
- 4. Practice building science within your limits of professional competency
- 5. Precautions when working around chemical biological and other potential hazards
- 6. Understand role and responsibilities of the building analyst professional
-
Section 1 Building Science Fundamentals
>
- BPI FIELD EXAM >
- BLOWER DOOR TEST >
- BPI BUILDING ANALYST STANDARDS >
-
BPI WRITTEN EXAM
>
- ESSENTIALS
- AFTER THE EXAM
- NEWSLETTER
- BLOG
|
Copyright 2023 Building Science Training Center LLC
|